What is Relationship Intelligence (RQ)? The engine that drives defining moments.
In 1956 a US senator who would go on to become president released a short book that quickly became a best-seller and later was awarded a Pulitzer Prize.
Profiles in Courage by John F. Kennedy centers on the defining moments of eight former senators — John Quincy Adams, Daniel Webster, Thomas Hart Benton, Sam Houston, Edmund G. Ross, Lucius Lamar, George Norris, and Robert A. Taft. Each of the profiled leaders made a decision to defy popular opinion, especially within their own party. Webster, for instance, spoke in favor of the Compromise of 1850, and Taft criticized the Nuremberg Trials for using retroactive laws when trying Nazi war criminals.
Reputations and legacies are made by those types of defining moments, but what makes the defining moments possible?
Many factors contribute, of course, but an overriding theme can be summed up in one word: Relationships. Opinions, insights, knowledge, character — all the things that come together in defining moments are shaped by relationships.

What is Relationship Intelligence (RQ)?
Relationship Intelligence is insight for adjusting your approach to make interactions more effective.
The biographies in Kennedy’s book, for instance, describe not just the courageous acts by the leaders he profiles, but the interactions between people that led to those acts. RQ is about making the most of those interactions because that leads to productive relationships and productive relationships result in important accomplishments.
A foundational component of RQ is that interactions happen in the moment, but relationships develop over time. A human relationship, in fact, is a connection between two or more people that is built on a foundation of shared experiences, interactions, and expectations — past, present, and future.
In other words, we can interact with people without being in a relationship with them. When a new employee joins a team, for instance, there are expectations for the future and daily interactions, but the relationships don’t develop until some shared experiences are created. The new employee and the other team members must get to know each other. And relationships end when there is no longer an expectation of future interactions.
Relationships develop over time
Since relationships develop over time, we can use three components to gauge the quality of a relationship:

Bad relationships often have a history of conflict and an expectation that things won’t get better and that not much will be accomplished together. Good relationships often include a history of disagreements and even some conflict, but the people involved have worked through such issues, work effectively together, and look forward to accomplishing shared goals.
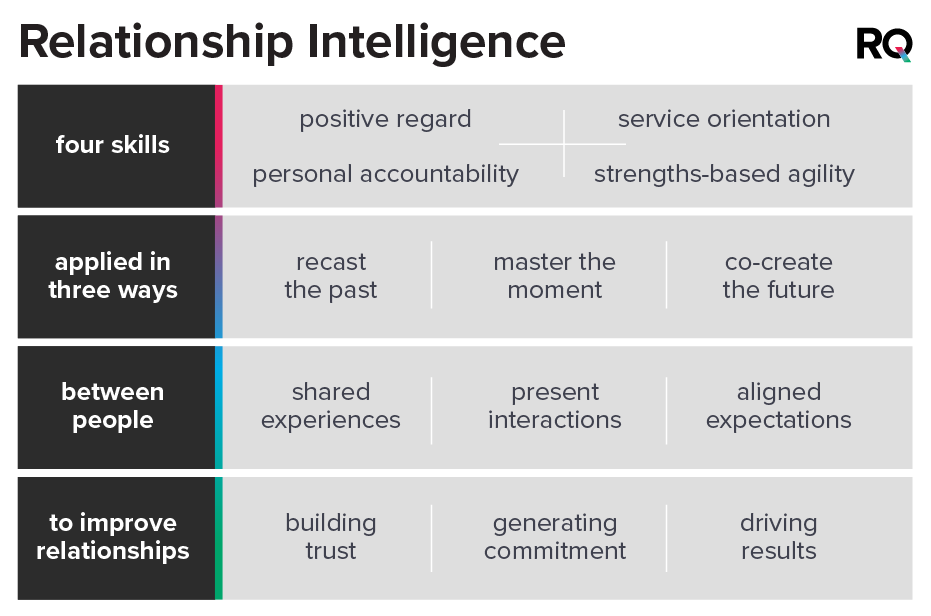
RQ helps you accomplish this by applying four skills in three ways to build trust, generate commitment, and drive results.
The four skills are positive regard, service orientation, personal accountability, and strengths-based agility. When people apply these in the past, present, and future aspects of their relationships, they can effectively recast the past, master the moment, and co-create the future. And that produces trust, commitment, and better results.
This model for RQ is more of a mosaic than a puzzle or a step-by-step process. The pieces work together in a harmonious manner.

Recasting the past is about viewing memories with new insights. It’s not about forgiving and forgetting, ignoring reality, or dismissing the past. It’s about adding information, exchanging perspectives, and challenging assumptions. It allows you to view past events in a more complete and inclusive way.

Mastering that moment involves practicing the four interrelated skills during interactions with other people. Those interactions might specifically involve recasting the past or co-creating the future, but shared experiences and aligned expectations also might simply be part of the context for your discussions and decisions.

Co-creating the future involves aligning your expectations in a relationship around shared purposes, values, and goals. The goals can include measurable outputs, but they also include expectations about the quality of the relationship. When you are in a relationship where there is alignment on what you want the future to hold, you are motivated to make it happen.
The key to effective RQ
Developing positive regard, service orientation, personal accountability, and strength-based agility and applying them in light of past experiences and future expectations is the key to effective RQ.
Positive regard
Positive regard means you believe all people (including yourself) have the capacity to reason and to make their own decisions, and that every person has a moral right to be treated with dignity and respect. This creates conditions where people are free to do their best.
This skill promotes inclusivity because it values diversity and refrains from prejudice and stereotype. People need to be accepted by others, and when they are accepted, they tend to grow, develop and flourish.
But positive regard isn’t just about how we view other people. In fact, to apply positive regard to others, we first need to have positive regard for ourselves.
Service orientation
Service Orientation is about creating lasting value in relationships, not only by serving others but by allowing others to be of service to you. It’s reciprocal. People with service orientation are curious and open to learning what other people need and are able to help other people succeed by being generous with their time and resources.
Personal accountability
Personal accountability recognizes that every person is in control of his or her choices and takes responsibility for the outcomes of those choices. Too often, managers think of accountability as something they must demand or impose, but personal accountability is an expression of freedom. When people make choices that are intended to produce results that are important to them, they become more accountable for their actions. Thus, managers who support personal accountability have positive regard for their direct reports and realize that promoting personal freedom is a form of service.
Strengths-based agility
Strengths-based agility is the intentional use of behavioral strengths in pursuit of desired outcomes. It’s like choosing the right tool for the job rather than seeing what tool you happen to have in your hand and searching for a place to use it. It is most effective, and more authentic when it is imbued with positive regard, service orientation, and personal accountability.
Developing your Relationship Intelligence and getting great results in your relationships means you will need all four skills working together as a system. When they do, relationships flourish. Shared experiences provide the proof required to build trust. Present interactions are marked by commitment. And there is alignment on expectations, so you get the results that become your defining moments.
To learn more about Relationship Intelligence, book a demo or watch our brief video.









